The advent of smartphones has brought about a revolutionary transformation in telecommunications, surpassing conventional expectations with their multifaceted utility. However, a recent report has unveiled a concerning trend: children now spend twice as much time on their smartphones as they do engaging in conversations with their parents.
This revelation is disconcerting, given the extensive role smartphones play in our daily lives. From facilitating online transactions and social messaging to e-banking and prolonged phone calls, our reliance on these devices is pervasive. Yet, amidst this technological dependency, it is imperative to pause and reflect on the safety and security of the data housed within our smartphones.
Regrettably, the reality is grim—every piece of data on your smartphone is susceptible to attack.
Consider the alarming fact that a child’s 10-digit phone number, seemingly innocuous, could potentially grant unauthorized access to text messages, phone conversations, and even location data. This vulnerability has manifested in the past and looms as a persistent threat in the future.
Enter the “SS7 Hack Attack,” a perilous breach facilitated by the Signaling System 7 (SS7) protocol. This protocol serves as the backbone for exchanging data between network devices in the global network infrastructure.
To illustrate, imagine making a phone call from Carrier A to a friend on Carrier B, situated at a distance. The seemingly routine act of transmitting voice messages between the two carriers becomes the conduit for potential exploitation in the form of the SS7 Hack Attack. In essence, this threat underscores the critical need for heightened awareness and security measures in the ever-expanding realm of smartphone usage.
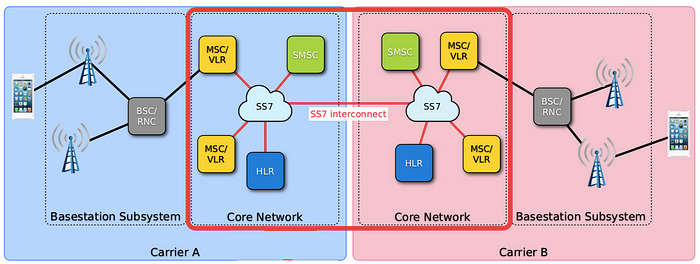
In the intricate web of telecommunications, phone signals travel from base stations to nearby towers and are subsequently transmitted to the SS7 network in Carrier A. Within the framework of the SS7 network, crucial components include the Home Location Register (HLR), housing subscriber information such as phone numbers and call/text data permissions, and the Visitors Location Register (VLR), which maintains a database of geographical locations in proximity to the subscriber.
The exchange of data between Carrier A and B is facilitated through these SS7 network devices, ultimately reaching the intended recipient. However, despite its integral role in global telecommunications, the SS7 protocol, employed by over 800 telecoms worldwide, stands vulnerable to exploitation due to its inherent lack of security measures.
The absence of an established security system within the SS7 network renders it easily compromised by hackers. Once unauthorized access is gained, a malicious actor can exploit a myriad of sensitive information, including:
- Listening and Recording Phone Calls: The hacker can eavesdrop on and record phone conversations.
- Reading SMS Messages: Both sent and received SMS messages become accessible to the intruder.
- Tracking Geographical Locations: The hacker can pinpoint the geographical location of the targeted subscriber.
Moreover, the compromised SS7 network provides a gateway for hackers to bypass two-factor authentication, typically sent via SMS. By intercepting the SMS messages on the network, a hacker can exploit the shared information for nefarious purposes.
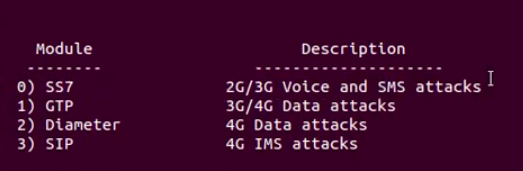
To execute such attacks, hackers delve deeper into the system, seeking a suitable provider for the targeted network. Tools like SigPloit, a signaling security testing framework, come into play. The installation process involves navigating to the SigPloit directory, installing necessary dependencies, and launching the framework. Within SigPloit, attackers can select the SS7 module, enabling them to exploit vulnerabilities in the signaling protocols and carry out the aforementioned intrusions.
This highlights the pressing need for enhanced security measures within the SS7 protocol to safeguard the integrity of telecommunications and protect users from unauthorized access and potential privacy breaches.
How do they Attack?
To attack, You need to dig deeper to find a suitable provider for your network.
SigPloit, a signaling security testing framework used to exploit vulnerabilites in the signaling protocols
1.1 Installing SigPloitcd SigPloitsudo pip2 install -r requirements.txtpython sigploit.py
1.2 Selecting the Module as SS7
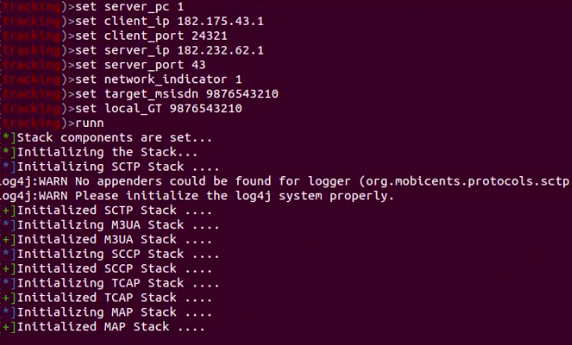
1.3 Setting the options:
client_pc, serve_pc, client and server IP, port, MSISDN (phone number)
1.4 Capturing packets from any packet analyzer
1.5 Gathering Information using “HackRF one” hardware tool.
Delving into the realm of WhatsApp, a ubiquitous messaging application with over 1 billion users across 180 countries, we find a platform that boasts end-to-end encryption. However, despite this robust security feature, the Achilles’ heel lies in the account verification process, which relies on SMS or mobile call authentication. Opportunistic hackers exploit this vulnerability by targeting the SS7 network.
In this scenario, if a hacker gains possession of your phone number and executes an SS7 attack to intercept your SMS verification messages, they can seamlessly gain unauthorized access to your WhatsApp account by associating it with their own account. This type of incursion is commonly referred to as a “Zero-day attack,” signifying its exploitability at its peak.
To counteract the threat posed by SS7 attacks, experts advocate for the implementation of a new methodology to replace the existing SS7 networks. However, a critical challenge surfaces as the SS7 vulnerability is not merely a flaw but was intentionally designed in such a susceptible manner.
In response to this ongoing concern, a German cybersecurity researcher devised a potential safeguard in the form of an Android application known as SnoopSnitch. This application serves as a proactive measure, aiming to detect and alert users to potential SS7 attacks on their mobile devices. While such innovations represent progress in mitigating vulnerabilities, the broader issue of revamping the fundamental infrastructure of SS7 networks remains an imperative step toward fortifying the security of communication platforms like WhatsApp.
In essence, surviving SS7 attacks necessitates a multifaceted approach that combines technological innovations, strategic replacements of vulnerable systems, and ongoing vigilance to stay one step ahead of evolving cybersecurity threats.
SnoopSnitch would collect and analyze mobile radio data to make you aware of your mobile network security and to warn you about threats like fake base stations, user tracking, and SS7 attacks.
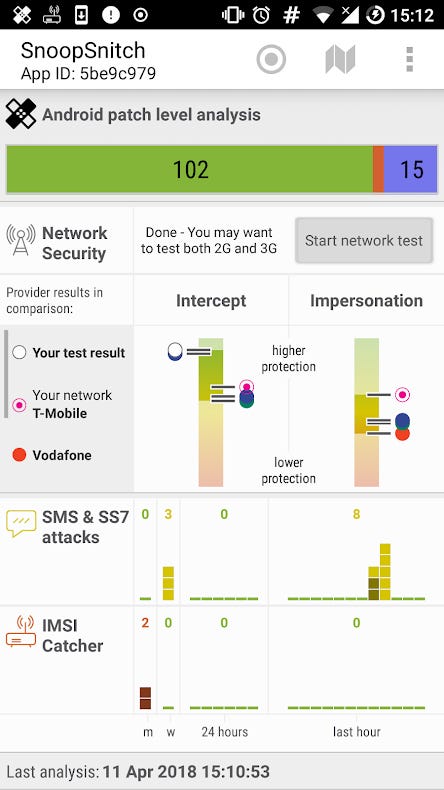
To install this application, the phone has to be rooted. Root privileges will be needed to collect mobile network data.
Currently, SnoopSnitch is compatible only with Android phones.
These are the web links that describe the incident that happened on the loophole of SS7 networks:
Although, SS7 Attacks cannot be prevented from the attack they can, however, be detected in Network Function Virtualisation using Machine Learning.
Detecting SS7 Attack using ML
This is a research paper contributed by Pentester Club Team!
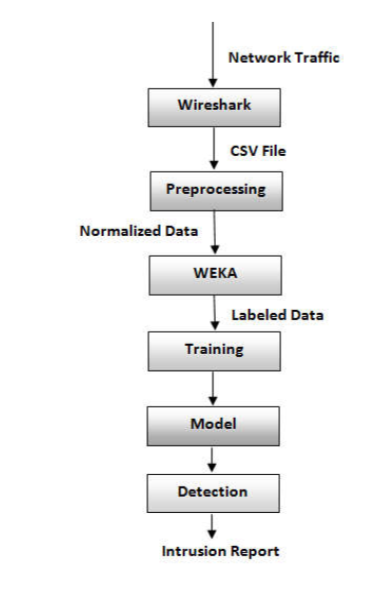
Their approach involved integrating machine learning into the analysis of SS7 network data, sourced through a packet analyzer. The data was subsequently exported in CSV format for preprocessing, transforming nominal data into numeric representations. The selection of appropriate algorithms was contingent upon the nature of the data, and for this purpose, they employed WEKA, a compilation of machine learning algorithms.
Four classifiers were deployed to generate models, and the results derived from each classification algorithm were meticulously scrutinized and evaluated. The emphasis was on identifying the fastest algorithm that yielded commendable results. This meticulous selection process ensured that the most efficient and effective algorithm was chosen for further application.
In essence, their methodology hinged on leveraging machine learning techniques to enhance the analysis of SS7 network data, employing a systematic approach that encompassed data preprocessing, algorithm selection, and thorough evaluation to ascertain optimal performance.
In conclusion, the 2018 report underscores the persistently low level of security in mobile communication networks. Initially perceived by many telecom companies as a low-level risk, the SS7 attack has proven otherwise, as unidentified hackers successfully exploited its vulnerabilities. Consequently, a cautionary stance is advised to ensure the safety and security of digital data.
A noteworthy aspect of digital security pertains to Google accounts, specifically the “Google Activity” feature. This feature meticulously logs a comprehensive spectrum of internet activities, encompassing browsing and search histories, physical locations, contact information, and additional details.
Of particular concern is the vulnerability in the event of a hacker attempting to access a Google account through the “forget password” option. In such a scenario, the hacker would encounter a 2FA (Two-Factor Authentication) verification process, which involves a 6-digit code sent via SMS. The SS7 network, however, stands as a potential weak point, as hackers can exploit it to intercept the SMS and gain unauthorized access.
In light of these vulnerabilities, maintaining a vigilant and proactive approach to digital security becomes paramount. Users are urged to stay informed about potential risks and employ additional measures to bolster the security of their online accounts and sensitive information.
Leave a Reply